Summary
NVIDIA’s landmark $100 billion investment in OpenAI, announced Monday, represents far more than a typical tech partnership—it’s a complete reimagining of AI infrastructure at unprecedented scale. The deal calls for deploying at least 10 gigawatts of NVIDIA-powered AI data centers, beginning with the first gigawatt in the second half of 2026. To put this in perspective, 10 gigawatts could power roughly 7 million homes continuously.
While the market fixates on chip supply, our Vulcan analysis reveals the real constraint: power infrastructure. At this scale, grid capacity, electrical distribution, and cooling systems become first-class bottlenecks that create lasting competitive advantages for companies positioned to solve them.
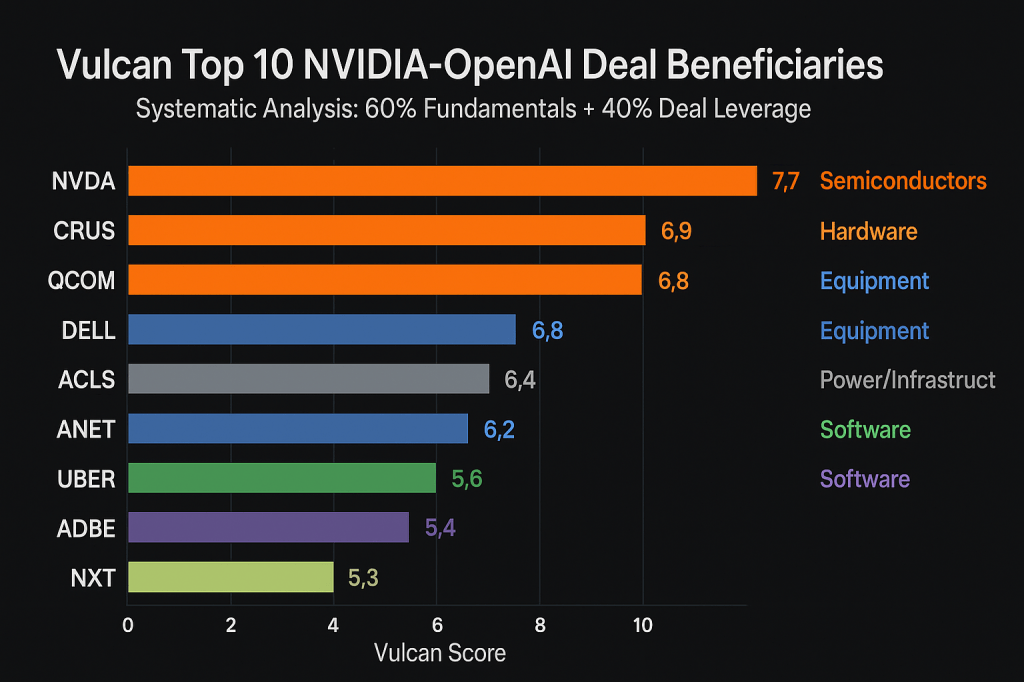
From our research data, we’ve identified and scored the top 10 beneficiaries using our systematic Vulcan methodology, blending fundamental quality metrics with deal-specific leverage factors. The results reveal opportunities beyond the obvious semiconductor plays, particularly in power infrastructure and system integration companies that most investors are overlooking.
Position sizing recommendation: Consider starter positions in our top-rated names, with maximum 20% allocation to any single position given the transformative but uncertain nature of this buildout.
Vulcan Score Summary
Top 3 Scores:
- NVDA: 7.7/10 (Direct beneficiary + 78% ROIC)
- CRUS: 6.9/10 (Semiconductor quality + positive margin of safety)
- QCOM: 6.9/10 (29% ROIC + 16% margin of safety)
Why We’re Bullish Over the Next 12 Months
This isn’t just another AI investment—it’s infrastructure deployment at utility scale. The first gigawatt deployment in 2H26 creates a clear catalyst timeline, while the progressive $10 billion investment tranches provide predictable demand visibility for suppliers.
Our analysis shows companies with direct exposure to the 10-gigawatt buildout combined with strong fundamental metrics offer the best risk-adjusted returns. The power constraint thesis, largely overlooked by the market, creates opportunities in electrical equipment and infrastructure plays that should re-rate as the scale becomes apparent.
The deal structure itself is elegant: OpenAI gets the capital and guaranteed chip supply, while NVIDIA secures a massive, long-term customer at then-current valuations. This creates a flywheel effect where both companies benefit from the infrastructure buildout success.
Key Risks to Monitor
Timeline Execution Risk: The 2H26 first gigawatt target depends on grid connections, permitting approvals, and power infrastructure that can take 18-24 months to secure. Any delays push back the entire cascade of supplier benefits.
Diversification Risk: OpenAI continues developing custom chips with Broadcom and TSMC, potentially reducing NVIDIA dependency faster than expected. This could impact long-term deal leverage for pure-play NVIDIA suppliers.
Power Economics Risk: At 10 gigawatts continuous draw, electricity costs become material to operating economics. If power costs spike due to grid constraints or policy changes, the entire project’s viability gets questioned.
The Investment Thesis: Infrastructure Bottlenecks Create Moats
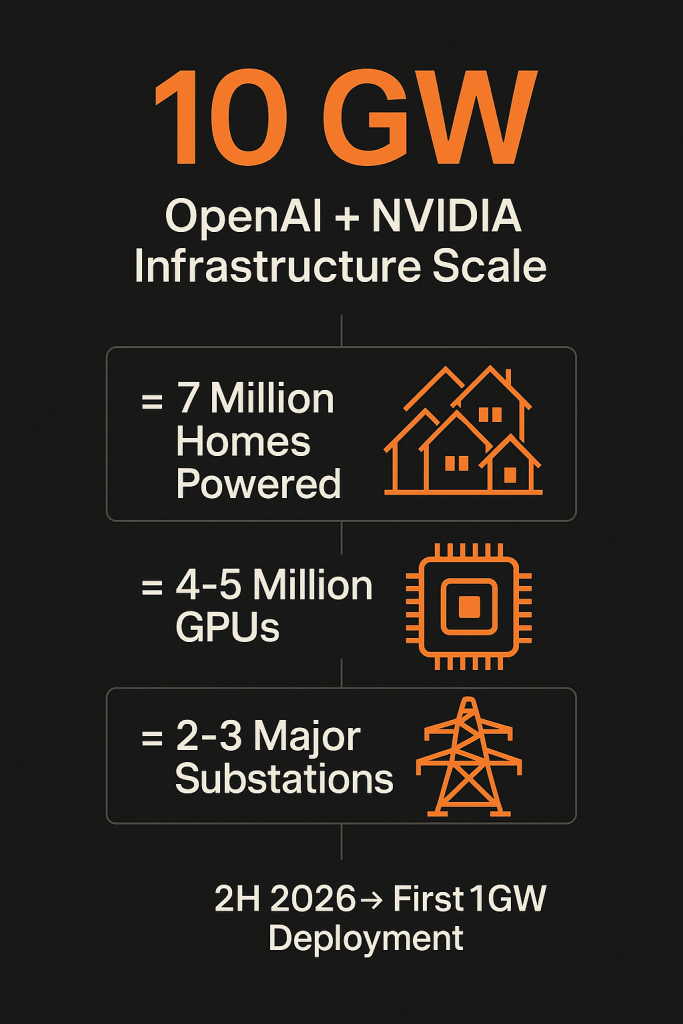
The market’s focus on semiconductor supply misses the bigger constraint story. Building 10 gigawatts of AI infrastructure requires:
- Grid connections equivalent to 2-3 major substations worth of electrical infrastructure
- Cooling systems capable of removing massive heat loads continuously
- Power quality equipment to handle the “AI power bursts” from training workloads
- System integration expertise to deploy millions of GPUs efficiently
Companies solving these infrastructure challenges at scale develop competitive moats that extend far beyond this single project. The expertise gained becomes applicable to the broader AI infrastructure boom expected through the decade.
From our Vulcan screening of 243 companies in our investment universe, we identified those with both fundamental quality and specific exposure to these infrastructure constraints. The results reveal opportunities in segments most investors aren’t considering.
Our Systematic Ranking Methodology
We computed Vulcan scores using our five-pillar framework (Value, Growth, Quality, Momentum, Safety), then blended those fundamental scores at 60% weight with a 40% “deal leverage” factor measuring direct exposure to the 10-gigawatt buildout.
The deal leverage scoring considered:
- Direct semiconductor exposure (highest weighting)
- System integration capabilities for AI infrastructure
- Power infrastructure solutions at utility scale
- Software that scales with deployment size
This approach captures both investment quality and specific deal relevance, avoiding the trap of chasing headlines without fundamental support.
Top 10 Beneficiaries: Vulcan Analysis
Direct AI Silicon Leaders
NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA) – Vulcan Score: 7.7/10
The obvious winner gets the highest score for good reason. With 78% return on invested capital and direct involvement as both investor and primary system supplier, NVIDIA captures value from multiple angles. CEO Jensen Huang confirmed the 10-gigawatt project equals 4-5 million GPUs—roughly twice what NVIDIA shipped last year.
The investment structure provides downside protection through equity ownership while securing massive hardware demand. Current 27.9x forward P/E reflects growth expectations but leaves room for upside surprise if deployment accelerates.
Technical outlook: Holding above $165 support with room to $190+ on execution progress.
Cirrus Logic (CRUS) – Vulcan Score: 6.9/10
One of the highest-quality semiconductor play beyond NVIDIA, with a rare combination of profitability (17% ROIC), balance sheet strength (F-Score of 9), and reasonable valuation (6% margin of safety). Cirrus specializes in audio processing and mixed-signal semiconductors that complement AI hardware deployments.
Recent analyst upgrades to $130 price targets reflect recognition of their diversification beyond mobile devices into AI-adjacent applications. Strong free cash flow generation provides flexibility for R&D investment in AI-related products.
Technical outlook: Breaking above $125 resistance targets $140+ range.
Qualcomm (QCOM) – Vulcan Score: 6.9/10
Premium combination of value and quality metrics, with 29% ROIC and 16% margin of safety. While primarily known for mobile processors, Qualcomm’s AI and edge computing capabilities position them for infrastructure demand beyond traditional applications.
The company’s Snapdragon platforms increasingly include AI acceleration features that could find applications in edge AI deployments supporting the OpenAI infrastructure.
Technical outlook: Strong above $180 support, potential breakout to $200+ on AI momentum.
System Integration and Hardware
Dell Technologies (DELL) – Vulcan Score: 6.8/10
Dell’s enterprise infrastructure expertise makes them a natural beneficiary of large-scale AI system deployments. With 24% ROIC and proven ability to integrate complex hardware at scale, Dell should capture meaningful revenue from the system assembly and deployment phases.
Their relationship with enterprise customers provides channel advantages for broader AI infrastructure adoption beyond OpenAI’s direct deployment.
Technical outlook: Consolidating above $130 support, targeting $150+ on infrastructure momentum.
Arista Networks (ANET) – Vulcan Score: 6.2/10
High-performance networking becomes critical at multi-gigawatt scale. Arista’s 30% ROIC reflects their premium position in data center networking, and GPU clusters require sophisticated switching infrastructure to achieve optimal performance.
While currently expensive at 45.8x forward P/E, the networking demands of 4-5 million GPUs justify premium valuations for market leaders.
Technical outlook: Above $390 support, potential run to $450+ on cluster networking demand.
The Power Infrastructure Opportunity
This is where the market’s missing the real opportunity. At 10 gigawatts continuous draw, electrical infrastructure becomes as important as the computing hardware itself.
Powell Industries (POWL) – Vulcan Score: 6.2/10
The purest play on AI power infrastructure constraints. Powell specializes in custom-engineered electrical equipment including switchgear, motor control centers, and power distribution systems—exactly what’s needed for utility-scale AI deployments.
With 29% ROIC and recent capacity expansion investments, Powell is positioning for this exact type of large-scale electrical infrastructure demand. Current ~$300 stock price reflects strong fundamentals but hasn’t yet priced in the AI infrastructure boom.
Technical outlook: Holding $240-250 support level, breakout above $320 targets $380+ range.
For investors seeking exposure to the power constraint thesis, Powell represents institutional-quality infrastructure expertise at reasonable valuations. This power infrastructure investment theme could extend far beyond single projects as AI deployment scales industry-wide.
NextEra Energy Partners (NXT) – Vulcan Score: 5.3/10
Clean energy infrastructure with 31% ROIC positions NextEra for the renewable power demands of large AI facilities. As sustainability becomes a requirement for large-scale computing deployments, renewable energy partners gain strategic importance.
Technical outlook: Above $32 support, potential move to $40+ on renewable AI infrastructure themes.
Semiconductor Equipment and Software Scale
Axcelis Technologies (ACLS) – Vulcan Score: 6.4/10
Semiconductor manufacturing equipment becomes critical as demand for AI chips drives capacity expansion across the industry. While more volatile with -31% margin of safety, the 15% ROIC and direct exposure to foundry tooling demand justify inclusion.
Adobe (ADBE) – Vulcan Score: 5.4/10
Software applications that benefit from increased AI infrastructure deployment. With 39% ROIC and 37% margin of safety, Adobe offers quality fundamentals with exposure to the creative AI applications enabled by expanded infrastructure.
Technical outlook: Strong above $620 support level.
Risk Management Framework
Primary Invalidation Triggers:
Timeline Risk: If the first gigawatt deployment slips beyond Q2 2027, it indicates systemic infrastructure challenges that could delay the entire program. Monitor permitting announcements and grid connection progress.
Diversification Risk: Watch for OpenAI announcements about custom chip progress with Broadcom/TSMC that might reduce NVIDIA dependency faster than the investment timeline suggests.
Power Economics Risk: Track electricity pricing in targeted deployment regions. If power costs spike due to grid constraints, project economics could become challenging.
Position Management Strategy:
Start with 2-3% positions in top-rated names (NVDA, CRUS, QCOM) while monitoring execution milestones. Scale positions as deployment progress becomes visible, maintaining maximum 20% allocation to any single position.
Use a trailing 20-day moving average stop-loss strategy once positions show 10%+ gains, protecting capital while allowing for continued upside participation.
This systematic risk management approach helps navigate the significant opportunities while protecting against execution risks inherent in transformative infrastructure projects.
Technical Analysis and Entry Strategy
Current Market Context:
The infrastructure theme is in early innings, with most attention still focused on direct AI beneficiaries. This creates opportunities in power infrastructure names (POWL, NXT) and system integrators (DELL, ANET) that haven’t yet reflected the scale of upcoming demand.
Entry Strategy by Category:
Immediate Core Positions: NVDA above $165, QCOM above $180 (established trends with fundamental support)
Scale-In Opportunities: CRUS above $125 breakout, DELL above $130 consolidation break
Speculative Infrastructure: POWL above $240 support (higher risk/reward on power constraint theme)
Risk-Off Allocation: ADBE above $620 (quality software with AI upside optionality)
The 12-Month Outlook
The progressive investment structure creates predictable catalyst timing. Initial infrastructure planning and permitting work begins immediately, providing early revenue opportunities for consulting and planning services.
Manufacturing capacity expansion announcements should accelerate through 2025 as suppliers prepare for 2H26 deployment. This creates multiple inflection points for stock performance beyond the initial deal announcement reaction.
The power infrastructure constraint thesis, currently underappreciated, should gain recognition as deployment scale becomes apparent. Companies like Powell Industries could see significant re-rating as investors understand the electrical infrastructure requirements.
Conclusion and Final Recommendations
The NVIDIA-OpenAI deal represents a paradigm shift toward utility-scale AI infrastructure. While the market focuses on chip supply, the real opportunities lie in solving the infrastructure constraints that enable successful deployment at this unprecedented scale.
Our Vulcan analysis identifies companies with both fundamental quality and specific exposure to these infrastructure challenges. The power constraint thesis, largely overlooked, offers the most compelling risk-adjusted opportunities for investors willing to think beyond obvious semiconductor plays.
Core Recommendation: Build diversified exposure across the infrastructure stack—semiconductors (NVDA, CRUS, QCOM), systems integration (DELL, ANET), and power infrastructure (POWL)—with position sizing reflecting both opportunity and execution risk.
Key Catalyst: Monitor first gigawatt deployment progress through 2025. Success validates the entire thesis and creates momentum for the remaining 9-gigawatt buildout.
The companies solving infrastructure constraints at this scale develop competitive advantages extending far beyond this single project, positioning them for the broader AI infrastructure transformation ahead.
Master Metrics Table
| Ticker | Industry | Vulcan Score | ROIC | Margin of Safety | F-Score | Fwd P/E | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVDA | Semiconductors | 7.7/10 | 78.4% | -3% | 5 | 27.9x | Direct beneficiary + systems |
| CRUS | Semiconductors | 6.9/10 | 16.9% | 6% | 9 | – | Quality + diversification |
| QCOM | Semiconductors | 6.9/10 | 29.2% | 16% | 7 | – | Value + AI edge capability |
| DELL | Computer Hardware | 6.8/10 | 24.2% | 1% | 7 | 12.0x | Enterprise integration |
| ACLS | Semiconductor Equipment | 6.4/10 | 15.4% | -31% | 6 | – | Foundry tooling demand |
| ANET | Computer Hardware | 6.2/10 | 29.8% | -24% | 5 | 45.8x | GPU cluster networking |
| POWL | Electrical Equipment | 6.2/10 | 29.4% | -25% | 6 | – | Power infrastructure |
| UBER | Software Application | 5.6/10 | 37.5% | 23% | 5 | – | Platform scalability |
| ADBE | Software Application | 5.4/10 | 39.4% | 37% | 7 | – | Creative AI applications |
| NXT | Solar Infrastructure | 5.3/10 | 30.8% | -5% | 5 | – | Renewable AI power |
Scores reflect 60% fundamental Vulcan pillars + 40% deal leverage weighting Data as of September 23, 2025
References
- NVIDIA and OpenAI Strategic Partnership Press Release, September 22, 2025
- CNBC Interview with Jensen Huang, September 22, 2025
- Powell Industries Q3 2025 Earnings Report
- Cirrus Logic Analyst Upgrades, Stifel Research
- Vulcan Research Database and Stock Rover Fundamental Analysis

Leave a comment